What is each compound’s systematic name? Embark on an enlightening journey into the fascinating realm of chemical nomenclature, where we unravel the secrets behind naming compounds systematically. Guided by the authoritative International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) guidelines, we delve into the intricacies of inorganic, organic, and coordination compounds, deciphering their systematic names and unraveling the hidden meanings behind their structures.
From the simplest ionic compounds to complex organic molecules, we explore the systematic naming conventions that govern the chemical world. Along the way, we uncover the role of functional groups and isomers in shaping compound names, gaining a deeper understanding of the relationship between structure and nomenclature.
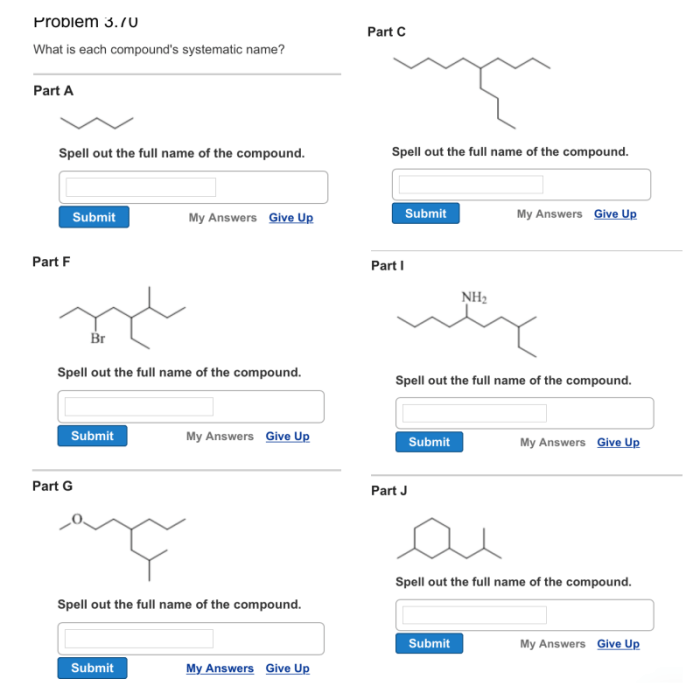
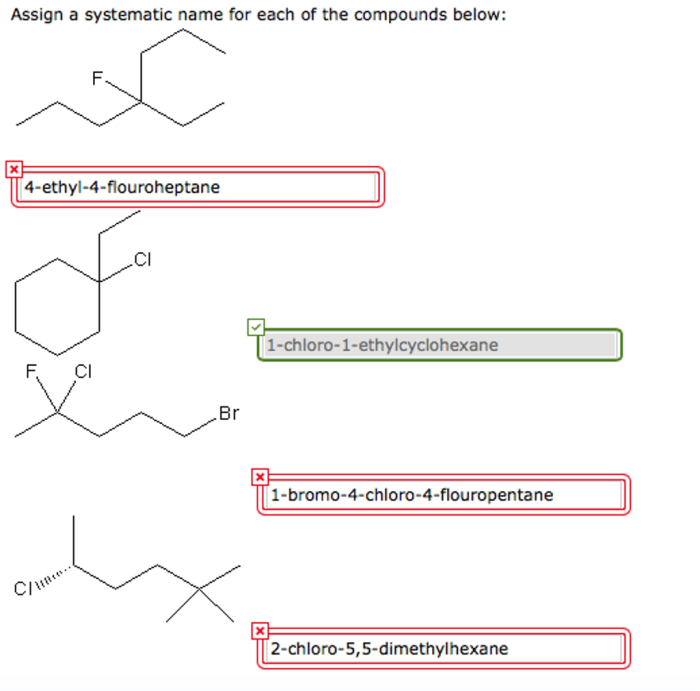
Compound Nomenclature: What Is Each Compound’s Systematic Name
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has developed a systematic naming system for compounds to ensure consistency and clarity in chemical communication. This system provides a set of rules for assigning unique names to chemical compounds based on their composition and structure.
Inorganic Compounds
Inorganic compounds are compounds that do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds. The systematic naming of inorganic compounds depends on the type of compound:
- Ionic Compounds:Consisting of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, are named by first naming the cation, followed by the anion. The name of the cation is typically the element’s name, while the anion’s name ends in “-ide”.
- Molecular Compounds:Composed of two or more nonmetal elements, are named by using the prefixes “mono-“, “di-“, “tri-“, etc., to indicate the number of atoms of each element, followed by the root of the element’s name, and ending with the suffix “-ide”.
- Coordination Complexes:Consisting of a metal ion surrounded by ligands, are named by first naming the ligands, followed by the metal ion. The name of the metal ion is typically the element’s name, while the name of the ligand depends on its structure and charge.
Organic Compounds
Organic compounds are compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen bonds. The systematic naming of organic compounds depends on the structure of the compound:
- Alkanes:Hydrocarbons with only single bonds, are named by using the prefix “alkan-” followed by the suffix “-ane” to indicate the number of carbon atoms in the chain.
- Alkenes:Hydrocarbons with one or more double bonds, are named by using the prefix “alken-” followed by the suffix “-ene” to indicate the number of carbon atoms in the chain and the location of the double bond.
- Alkynes:Hydrocarbons with one or more triple bonds, are named by using the prefix “alkyn-” followed by the suffix “-yne” to indicate the number of carbon atoms in the chain and the location of the triple bond.
- Aromatic Compounds:Compounds that contain a benzene ring, are named by using the prefix “phenyl-” or the suffix “-benzene” to indicate the presence of the benzene ring.
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms that give organic compounds their characteristic properties. The systematic naming of organic compounds often includes the name of the functional group, which is added to the base name of the compound.
- Alcohol:Contains a hydroxyl group (-OH)
- Aldehyde:Contains a carbonyl group (-CHO)
- Ketone:Contains a carbonyl group (-CO-)
- Carboxylic Acid:Contains a carboxyl group (-COOH)
- Amine:Contains an amino group (-NH2)
Isomerism, What is each compound’s systematic name
Isomerism is the phenomenon where compounds have the same molecular formula but different structures. Systematic naming of isomers requires specifying the specific structure of the compound.
- Structural Isomers:Compounds with the same molecular formula but different connectivity of atoms.
- Stereoisomers:Compounds with the same molecular formula and connectivity but different spatial arrangements of atoms.
FAQ
What is the importance of systematic compound naming?
Systematic compound naming provides a standardized and unambiguous way to identify and describe chemical compounds, facilitating communication and understanding among scientists.
How does IUPAC determine the systematic name of a compound?
IUPAC establishes guidelines based on the compound’s structure, considering factors such as the presence of functional groups, prefixes, and suffixes.
What is the difference between an empirical formula and a systematic name?
An empirical formula indicates the elemental composition of a compound, while a systematic name provides a more detailed description of its structure and connectivity.