The density of titanium is 4.51 g/cm3 – The density of titanium, a remarkable 4.51 g/cm3, sets it apart as a unique and versatile material. This exceptional density contributes to titanium’s widespread use in diverse industries, from aerospace to medical implants.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the concept of density, examining the factors that influence it and highlighting the significance of titanium’s density in various applications. We will also compare titanium’s density to other common materials, providing insights into its unique properties and advantages.
Definition and Concept of Density
Density is a physical property that quantifies the mass of a substance per unit volume. It is expressed in units such as grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). The formula for calculating density (ρ) is:
ρ = m/V
where m is the mass and V is the volume.
Density of Titanium

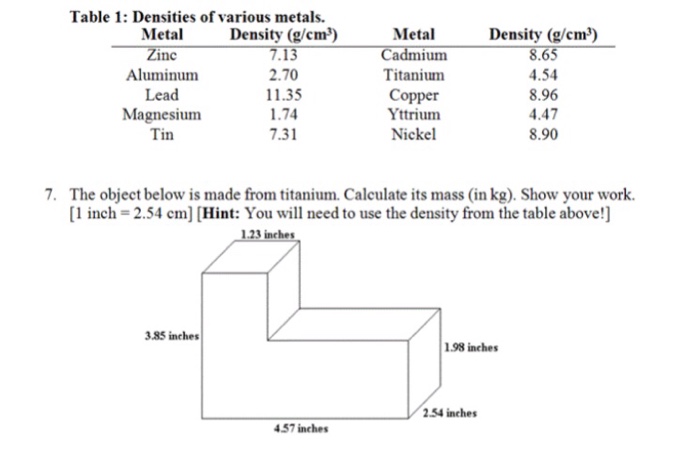
The given density of titanium is 4.51 g/cm³. This means that for every cubic centimeter of titanium, there is a mass of 4.51 grams. The density of titanium is an important factor in its various applications, such as aerospace, medical implants, and other industries.
Factors Affecting Density: The Density Of Titanium Is 4.51 G/cm3
Several factors can affect the density of a material, including:
- Temperature: As temperature increases, the density of most materials decreases due to thermal expansion.
- Pressure: High pressure can increase the density of a material by compressing its structure.
- Impurities: The presence of impurities can affect the density of a material, either increasing or decreasing it depending on the nature of the impurity.
For titanium, impurities such as oxygen and nitrogen can increase its density.
Applications of Titanium’s Density
The density of titanium is a crucial factor in its applications in various industries:
- Aerospace: Titanium’s high strength-to-weight ratio, due to its low density, makes it ideal for aircraft and spacecraft components.
- Medical Implants: Titanium’s biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, combined with its low density, make it suitable for medical implants, such as artificial joints and dental implants.
- Other Industries: Titanium’s density also plays a role in its use in sporting goods, jewelry, and chemical processing equipment.
Comparison with Other Materials

The table below compares the density of titanium to other common materials:
| Material | Density (g/cm³) |
|---|---|
| Titanium | 4.51 |
| Steel | 7.85 |
| Aluminum | 2.70 |
| Lead | 11.34 |
Titanium’s relatively low density compared to other materials, such as steel, makes it a desirable choice for applications where weight reduction is a priority.
FAQ Section
What is the significance of titanium’s density?
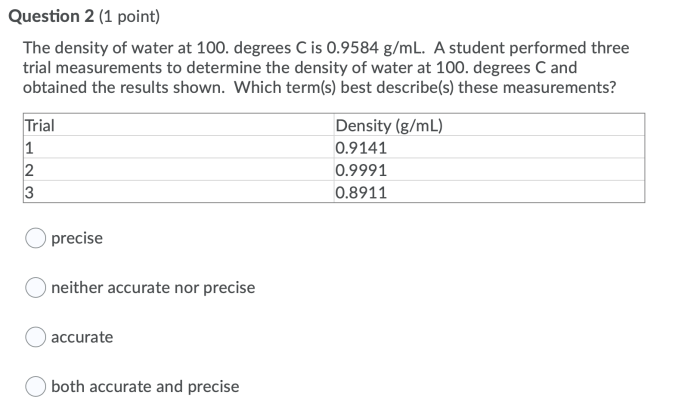
Titanium’s density, 4.51 g/cm3, plays a crucial role in its applications. This unique density makes titanium both strong and lightweight, allowing it to withstand high stresses while maintaining a relatively low weight.
How does temperature affect the density of titanium?
Temperature can influence the density of titanium. As temperature increases, the atoms in titanium vibrate more, causing the material to expand and its density to decrease.
What are the advantages of using titanium in aerospace applications?
In aerospace applications, titanium’s low density and high strength-to-weight ratio are highly advantageous. These properties enable the construction of lightweight and durable aircraft components, reducing fuel consumption and improving overall performance.