Embark on a scientific odyssey with our comprehensive Periodic Table and Trends Worksheet, meticulously crafted to unravel the enigmatic tapestry of chemical elements. Prepare to delve into the intricacies of atomic structure, periodic trends, and the predictive power of the periodic table, gaining invaluable insights into the fundamental principles that govern the behavior of matter.
This meticulously curated worksheet provides a comprehensive exploration of the periodic table, empowering you to decipher the intricate relationships between atomic number, electron configuration, and chemical properties. Delve into the fascinating periodic trends that govern atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity, unraveling the patterns that shape the chemical landscape.
Periodic Table and Trends
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. It is generally accepted that the modern periodic table was first published by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, although several other scientists had developed similar tables prior to this.
Atomic Number, Electron Configuration, and Chemical Properties
The periodic table is organized by atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Elements with the same atomic number are in the same column, or group, of the periodic table. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost shell of the atom.The
periodic table is also organized by electron configuration, which is the arrangement of electrons in the different energy levels of an atom. Elements with similar electron configurations are in the same row, or period, of the periodic table. Elements in the same period have similar physical properties, such as atomic radius and ionization energy.
Periodic Trends
There are several periodic trends that can be observed in the periodic table. These trends include:
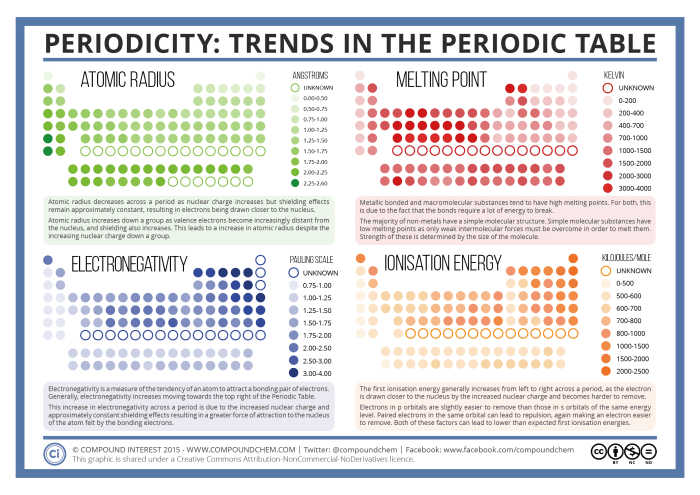
- Atomic radius: The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electron shell. Atomic radius generally increases down a group and decreases across a period.
- Ionization energy: Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. Ionization energy generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Electronegativity: Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons. Electronegativity generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
These periodic trends can be explained by the quantum mechanical model of the atom.
Properties and Reactivity of Elements
The periodic table is a powerful tool for predicting the properties and reactivity of elements. By examining an element’s position in the table, we can make inferences about its physical and chemical characteristics.
Physical Properties
The physical properties of elements vary depending on their position in the periodic table. Metals, found on the left side of the table, are typically shiny, malleable, and ductile. Nonmetals, located on the right side of the table, are often dull, brittle, and poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Metalloids, found along the diagonal line separating metals from nonmetals, exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals.
| Group | Period | Element | Physical Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | Lithium | Silvery-white, soft, and reactive metal |
| 17 | 2 | Fluorine | Pale yellow, highly reactive nonmetal gas |
| 14 | 3 | Silicon | Gray, brittle metalloid |
| 16 | 3 | Sulfur | Yellow, nonmetal solid |
| 15 | 3 | Phosphorus | White or red, highly reactive nonmetal |
Chemical Reactivity
The reactivity of an element is also influenced by its position in the periodic table. Elements in Group 1 (alkali metals) are highly reactive and readily form ions by losing an electron. Elements in Group 17 (halogens) are also highly reactive and readily gain an electron to form ions.
In general, reactivity decreases from left to right across a period and increases from top to bottom within a group.
The periodic table is an invaluable tool for understanding the properties and reactivity of elements. By examining an element’s position in the table, we can make predictions about its physical and chemical characteristics, enabling us to better understand and utilize the elements in various scientific and technological applications.
Periodic Table as a Predictive Tool
The periodic table is not merely a catalog of known elements; it is also a powerful tool for predicting the properties and reactivity of unknown elements. This predictive power arises from the periodic trends that govern the behavior of elements.
One of the most important periodic trends is the variation in atomic radius. Atomic radius generally increases down a group and decreases across a period. This trend can be used to predict the relative size of an unknown element based on its position in the periodic table.
Another important periodic trend is the variation in electronegativity. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons. Electronegativity generally increases across a period and decreases down a group. This trend can be used to predict the relative reactivity of an unknown element based on its position in the periodic table.
Examples of Predictive Power
The periodic table has been used to predict the properties and reactivity of many new elements. For example, in 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted the existence of an element that he called eka-silicon. He predicted that eka-silicon would have an atomic weight of 72 and would be a solid with a high melting point.
In 1875, a new element was discovered that matched Mendeleev’s predictions. This element was named germanium.
The periodic table has also been used to predict the properties of superheavy elements. Superheavy elements are elements with atomic numbers greater than 104. These elements are not found in nature and must be synthesized in the laboratory. The periodic table can be used to predict the properties of superheavy elements based on their position in the periodic table.
Applications of Periodic Trends
Periodic trends play a crucial role in various scientific and technological fields, providing a framework for understanding and predicting the properties and behavior of elements. These trends have led to significant advancements in chemistry, materials science, and medicine, among others.
Chemistry
In chemistry, periodic trends guide the design and synthesis of new materials with tailored properties. For example, the periodic table helps predict the reactivity of elements, enabling chemists to develop catalysts that enhance chemical reactions and optimize industrial processes.
Materials Science, Periodic table and trends worksheet
Materials scientists leverage periodic trends to create advanced materials with specific properties, such as strength, conductivity, and thermal stability. By understanding the relationship between an element’s position in the periodic table and its properties, researchers can design materials for applications ranging from electronics to aerospace.
Medicine
In medicine, periodic trends contribute to the development of new drugs and therapies. The periodic table provides insights into the biological activity of elements, guiding the design of drugs that target specific molecular targets and minimize side effects.
Question & Answer Hub: Periodic Table And Trends Worksheet
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
What are periodic trends?
Periodic trends are the规律性variations in physical and chemical properties of elements that occur as a function of their position within the periodic table.
How can the periodic table be used to predict the properties of an element?
The periodic table can be used to predict the properties of an element based on its position within the table. For example, elements in the same group (vertical column) tend to have similar chemical properties.